Understanding FN Biological Characteristics of Fibronectin
- Important components of cells and stroma
-
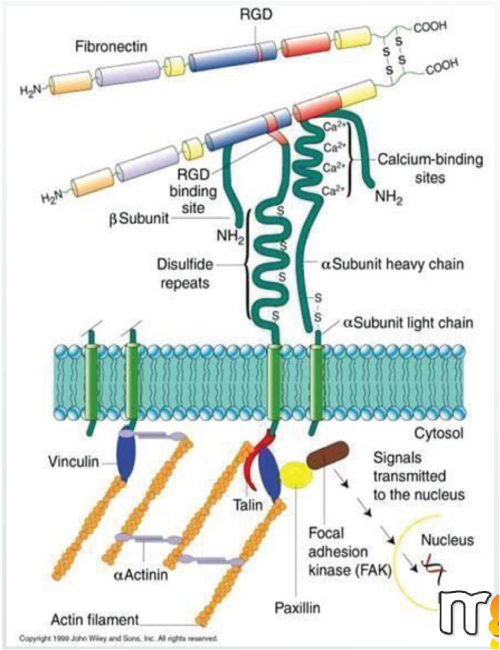
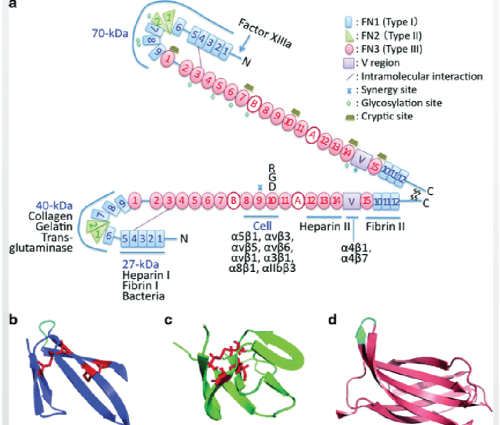
Double chain structure, six functional areas and unique RGD sequence
-
Construction of cell regeneration environment by combining 11 Integrins
- Regeneration and repair of epidermis, dermis, fibers, nerves, blood vessels, pigment and other cells
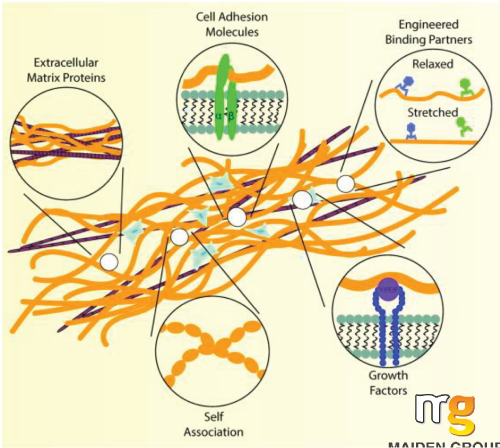
- It has strong compatibility and can cooperate with various biological components
- Fibronectin(FN) binds a large number of cell adhesion receptors, growth factors, and extracellular matrix proteins.
-
As a result, it has been implicated in mediating a range of cell activities, including migration, growth, adhesion, and differentiation
- FN binds to organisms such as S. aureus, S. epidermidis, and Streptococcus pyogenes to promote their interactions with phagocytic cells, including macrophages and neutrophils.
- Already circulating in blood and its concentration increases during wound occurrence.
FN participates in the whole process of wound healing
- Coagulation stage
- Inflammatory reaction
- Angiogenesis
- Granulation
- Tissue reconstruction
FN and Coagulation
Conclusion:
-
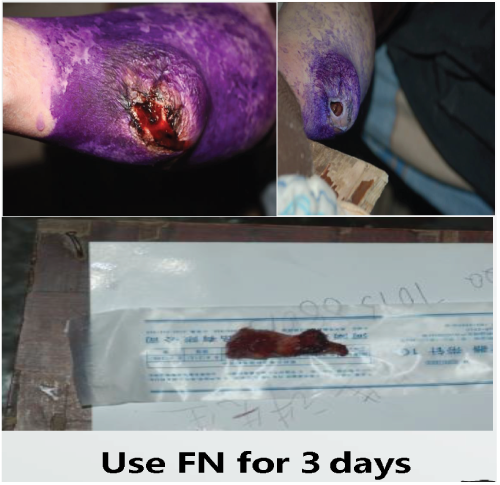
Hemophilia is a bleeding disease with hereditary coagulation dysfunction.
- It is proved that FN has a strong coagulation effect by controlling hemophilia patients' bleeding within 3 days